We explore the assembly of quantum dots in new quantum-dot solids. These materials, assembled from solution-processable building blocks, hold great promise for new optoelectronic devices due to their ease of production, high tunability and flexibility. Because of their quantum confinement, quantum dots have distinct energy levels just like atoms, and their assembly into periodic structures leads to new energy bands, so-called “minibands”, analogues of bands and electronic states in solids. Contrary to atoms, this mini-band structure can be easily “designed” by the properties and mutual interaction of the building blocks. Yet, such design requires insight into the assembly of quantum dots, the role of surface chemistry in the coupling of the quantum dots, and the resulting optoelectronic properties.
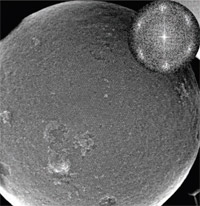
Kinetics of superball assembly
In this project, we investigate the q-dot assembly in-situ by x-ray scattering. This allows us not only to monitor the evolution of the structure, but also to extract the interactions of the assembling quantum dots. Read more …
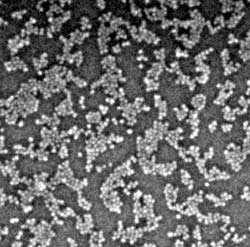
Epitaxial deposition of quantum dots
Critical Casimir forces allow controlled deposition of quantum dots on a substrate. We explore this deposition as a function of the crucial parameters, solvent correlation length and Debye screening length. Read more …
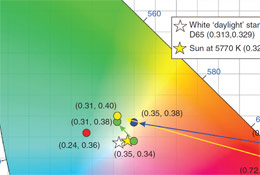
Multichromatic silicon nanocrystals
In collaboration with K. Newell, we show that we can achieve multichromatic silicon nanocrystals by electron-beam irradiation. Read more …

Ball-milled silicon nanocrystals
Ball milling leads to large quantities of silicon nanocrystals with surprising photoluminescent properties. Read more …
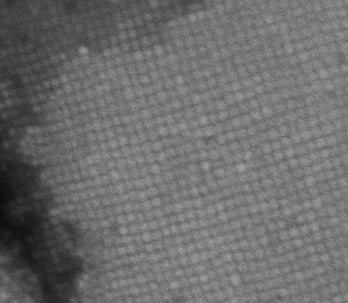
Emulsion assembly of perovskite nanocrystals
We assemble perovskite nanocrystals into superstructures such as superballs, superhexagons and supercubes by using oil-in-fluorinated oil emulsions.
Read more …
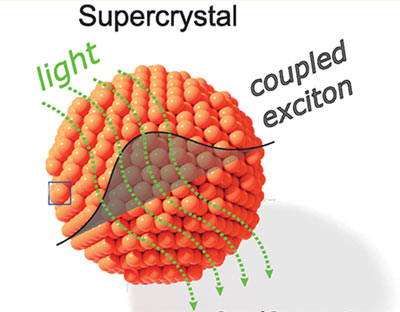
Photonic and excitonic coupling in quantum-dot supercrystals
A limitation of quantum dots for device applications is their low absorption cross section and conductivity. We show that large supercrystals assembled from CdSe quantum dots can exhibit efficient photonic and excitonic coupling. Read more …
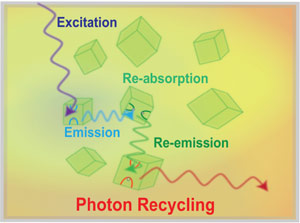
Photon recycling in all-inorganic perovskite nanocrystals
Photon recycling (PR), the repeated absorption and emission of photons in a medium, present a means to increase solar cell efficiency by keeping photons in the active layer. We find very efficient PR in perovskite nanocrystals, adding to their very beneficial properties. Read more …
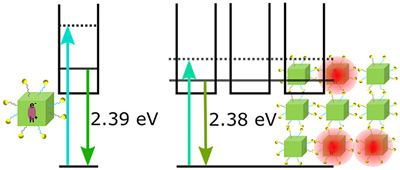
Electronic coupling in ordered perovskite nanocrystals superstructures
We demonstrate the electronic coupling of perovskite nanocrystals, densely packed in supercrystals. Transient absorption spectroscopy is used to reveal signatures of collective band like states. Read more …